Which are the top two reliable and popular investing strategies in India? I want to present two important investment options: the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) and the Public Provident Fund (PPF). Both investment alternatives are expanding significantly in the Indian market, but there are several distinctions you should be aware of.
To simplify things, we've created an article that gives you the knowledge you need to decide between PPF and EPF. We will discuss the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each plan so that you can position yourself to have worry-free financial security down the road.
What is EPF?
The EPF is one of the best retirement saving options, specially designed for Indian employees. The Employees' Provident Fund Organization (EPFO) handles the overall management and eventually receives contributions from both employers and employees.
When workers participate in employer matching, a portion of their earnings—typically 12 percent—is deducted and deposited into their employee-provided funds account (EPF). Every year, the fixed interest rate that EPF offers is reviewed by the government.
This fund provides supplementary benefits, such as insurance and pension plans, to ensure employees have financial stability in retirement.
What is PPF?
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is a long-term savings and investment plan designed and developed by the Indian government. It offers a trustworthy and secure way to save money for unforeseen expenses.
PPF is the greatest choice for risk-averse individuals searching for long-term investments with guaranteed returns and tax benefits. It is suitable for long-term financial goals like retirement planning or children's education since it encourages the steady buildup of a substantial corpus.
Benefits of EPF
- Employer Contribution: One of the primary advantages is matching employee contributions to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF). This effectively doubles the investment without requiring the employee to work more hours.
- Advantages of taxes: After five years of continuous employment, an employee's EPF interest is tax-free, and Section 80C of the Income Tax Act permits tax deductions on contributions.
- Fixed Interest Rate: The government reviews and announces the EPF's fixed interest rate once a year in order to guarantee a consistent return on investment.
- Extra perks: Besides the savings component, the Employee Provident Fund (EPF) offers insurance and pension plans as perks. These programs offer total financial stability for retirement.
- Partial Withdrawals: The EPF offers flexible access to funds for specific needs, such as marriage, education, urgent medical treatment, and home loan repayment.
Benefits of PPF
- Tax Exemptions: Because contributions are deductible under Section 80C and the interest and maturity amount are free from taxes, PPF is a tax-efficient investment.
- Government-Backed Security: Because the government supports PPF and ensures that the money invested is safe, it's a low-risk investment option.
- Attractive Interest Rates: PPF provides an alluring annual compound interest rate that boosts the long-term growth of the investment.
- Contribution Flexibility: With a minimum investment of ₹500 and a maximum commitment of ₹1.5 lakh every financial year, PPF is accessible to a wide range of investors.
- Loan and Partial Withdrawal Facilities: Between the third and sixth fiscal years, investors may borrow against their PPF account to provide liquidity. After the seventh fiscal year, they may withdraw a portion of their holdings.
Limitations of EPF
- Exclusively Relevant to Salaried Workers: Only employees who work for companies that have registered with the EPF are able to make an EPF investment.
- Fixed Contribution Rate: Base pay and additional allowances are immediately deducted from employees' 12% contribution rate.
- Restrictions on Withdrawals: With EPF, complete withdrawals are not allowed, and that is also the case in certain conditions, like upon retirement, unemployment, or fulfilling certain service tenure requirements. This restricts the amount of money that can be taken out immediately.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Since the government examines and announces the interest rate annually, changes in interest rates may affect the total returns on the Employee Provident Fund (EPF). As a result, the rate may change or even fall in some years.
- Complicated Transfer Process: Transferring an EPF account when moving jobs can be laborious and time-consuming, which may cause delays and issues with fund administration.
Limitations of PPF
- Extended Lock-in time: The PPF has a 15-year lock-in time, after which the money is locked away and cannot be released unless they are significantly removed before then. This results in a loss in liquidity.
- Low Contribution Limit: The PPF maximum contribution amount for each fiscal year is ₹1.5 lakh. This ceiling may be a barrier for those who want to invest more to take advantage of tax advantages or larger profits.
- Fixed Maturity Tenure: The PPF's 15-year maturity period may be too rigid for individuals needing to access their savings sooner or modify their investing plan over time.
- Interest Rate Variability: Although the government supports PPF, interest rates are subject to regular reviews and fluctuations that may affect returns.
- No Employer Contribution: Unlike EPF, PPF does not need employer contributions. Therefore, each individual is responsible for covering the full cost of investments.
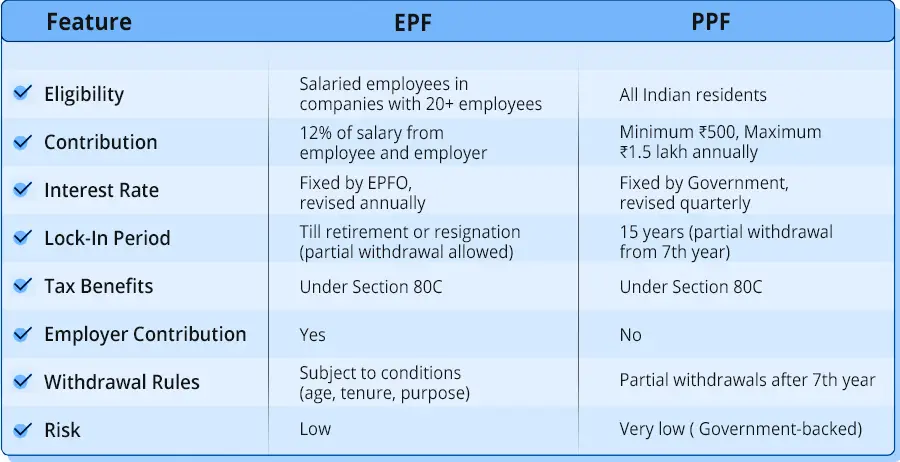
Comparison Table for EPF vs. PPF
Importance of EPF and PPF Calculators
It's critical to comprehend the possible returns on your assets when making financial plans for the future. You must adopt an EPF calculator and a particular PPF calculator in this situation. Based on your contributions, these online tools assist you in estimating the maturity amount and interest earned.
If you plan to calculate the EPF, try HR HUB's EPF Interest Rate Calculator. The good part is that HR HUB provides a responsive PPF Interest Rate Calculator. So, you can utilize both calculators from one platform.
EPF vs PPF: Which is the Best?
Your work situation and personal financial objectives mostly influence the decision between PPF and EPF. Company-provided benefits (EPF) offer salaried persons a stable retirement savings plan enhanced by company contributions and supplementary benefits such as insurance and pension plans. Indeed, because of its tax benefits, government security, and flexibility, PPF is preferable for salaried employees and independent contractors.
Thoroughly understanding the features, advantages, and disadvantages of both PPF and EPF will help you make an informed decision that will help you achieve your long-term financial goals. The ideal investing choice ultimately provides retirement financial security and peace of mind.